Ecology and Physical Setting
Boreal Outcrops are craggy openings in otherwise unbroken expanses of forest in the cooler regions of the state. They are often on mountain summits above 1,800 feet that are not high or exposed enough to support Alpine Meadow. Boreal Outcrops are often favorite hiking destinations—they offer commanding views of the surrounding northern forest and the valleys below. The outcrops are generally small, convex areas on hilltops. They are kept naturally open because of persistent drought, exposure to wind, loss of soil resulting from past fires or other disturbance, or a combination of these influences.
Vegetation
Boreal Outcrops are very sparsely vegetated, with scattered low trees such as red spruce, American mountain ash, and heart-leaved paper birch. Low shrubs include velvetleaf blueberry, bush honeysuckle, and black chokeberry. Dry site grasses, such as poverty grass and hairgrass, are rooted in small areas of accumulated soil. Other herbs include three-toothed cinquefoil and brownish sedge. Bryophytes and lichens, especially reindeer lichens, are usually abundant. In pockets where moisture accumulates, the moss Sphagnum russowii can form small peaty mounds.
Wildlife Habitat
Boreal Outcrops are harsh and exposed places. White-throated sparrows build nests on the ground, often in the cover of small patches of red spruce or blueberry. The rare boreal long-lipped tiger beetle is known to inhabit exposed bedrock areas in Vermont mountains. Boreal Outcrops are probably used most by wildlife that are associated with the adjacent forests of spruce and fir, including red squirrels, snowshoe hares, yellow-rumped warblers, and dark-eyed juncos.
Conservation Status and Management Considerations
Boreal outcrops are common in Vermont, and many examples are conserved. Some of the best examples, such as the summits of Mount Abraham and Mount Hunger (both of which host rare plants), are popular hikes and should be managed to avoid trampling of vegetation.

Related Communities
- Alpine Meadow occurs above treeline, generally above 3,500 feet. Alpine Meadows have a characteristic set of plants that are adapted to their colder, wetter climate.
- Boreal Acidic Cliff and Boreal Calcareous Cliff have slopes greater than 60 degrees, but share many species in common with Boreal Outcrop.
Distribution/Abundance
This is a widespread community in the cooler regions of Vermont, especially at higher elevations. Most examples are quite small. Similar communities are common throughout the region.
Characteristic Plants
Trees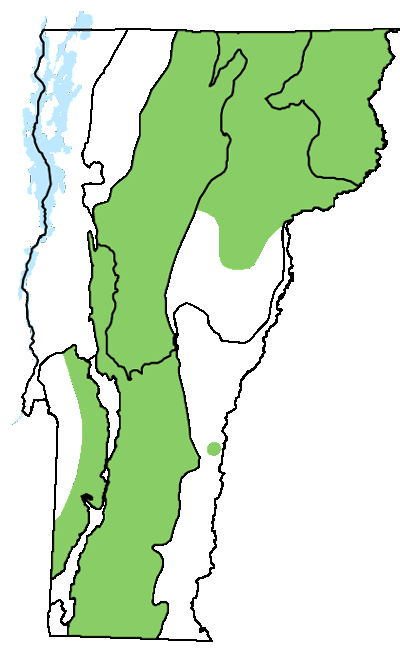
Red spruce – Picea rubens
Heart-leaved paper birch – Betula cordifolia
Balsam fir – Abies balsamea
American mountain ash – Sorbus americana
White pine – Pinus strobus
Red maple – Acer rubrum
Paper birch – Betula papyrifera
Shrubs
Velvetleaf blueberry – Vaccinium myrtilloides
Bartram’s shadbush – Amelanchier bartramiana
Bush-honeysuckle – Diervilla lonicera
Sheep laurel – Kalmia angustifolia
Black chokeberry – Aronia melanocarpa
Wild raisin – Viburnum nudum var. cassinoides
Mountain holly – Ilex mucronata
Herbs
Poverty grass – Danthonia spicata
Hairgrass – Deschampsia flexuosa
Canada mayflower – Maianthemum canadense
Bracken fern – Pteridium aquilinum
Sarsaparilla – Aralia nudicaulis
Brownish sedge – Carex brunnescens
Three-toothed cinquefoil – Sibbaldia tridentata
Bryophytes and Lichens

rocky places.
Reindeer lichen – Cladonia/Cladina spp.
Haircap moss – Polytrichum spp.
Moss – Sphagnum russowii
Non-native Plants
Sheep sorrel – Rumex acetosella
Canada bluegrass – Poa compressa
Rare and Uncommon Plants
Bigelow’s sedge – Carex bigelowii
Alpine bilberry – Vaccinium uliginosum
Appalachian firmoss – Huperzia appressa
Showy mountain ash – Sorbus decora
Boreal bentgrass – Agrostis mertensii
Black crowberry – Empetrum nigrum
Mountain cranberry – Vaccinium vitis-idaea
Associated Animals
Snowshoe hare – Lepus americanus
White-throated sparrow – Zonotrichia albicollis
Rare and Uncommon Animals
Boreal long-lipped tiger beetle – Cicindela longilabris
Places to Visit
Mount Hunger, Worcester, CC Putnam State Forest, Vermont Department of Forests, Parks, and Recreation (VDFPR)
Mount Abraham, Lincoln, Green Mountain National Forest (GMNF)
Mount Ascutney, Weathersfield, Mount Ascutney State Park, VDFPR
Bald Mountain, Bennington, GMNF
