Ecology and Physical Setting 
Rich Fens are hotspots of botanical diversity—they are great places to see beautiful and uncommon orchids. The high species richness of these fens results from the naturally open condition and the constant inputs of calcareous groundwater.
Rich Fens typically occur on gentle slopes and have shallow peat accumulations of less than three feet, although in some cases the peat is deeper. The peat is saturated throughout the growing season, and there may be small, shallow pools scattered over the generally concave surface of the fen. Areas of groundwater seepage are usually evident at the upslope margins of Rich Fens where there may be small pools or springs adjacent to the sharp transition to upland forest. This seepage water moves slowly across the fen through the upper layers of peat. It is rich in calcium and has pH ranging from 5.8 to 8.0. Rich Fens occur only in areas of calcium-rich bedrock. In this less acidic, more oxygenated environment, peat tends to be more decomposed than in Intermediate Fens, but sedge and moss fragments are still recognizable.
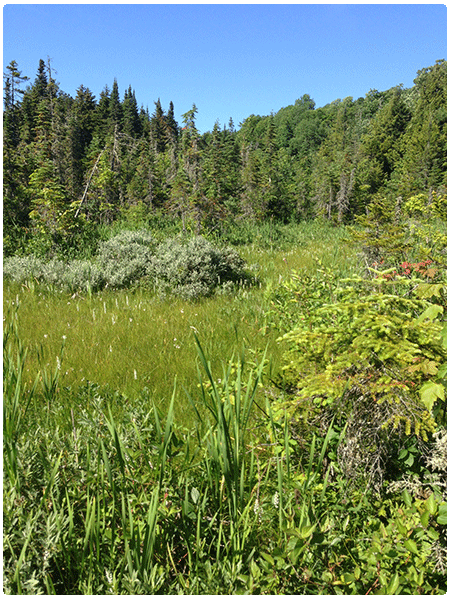 Rich Fens may occur in isolation from other wetlands or as part of larger wetland complexes. Rich Fens are commonly found in small depressions, with very small surface watersheds, and typically form the headwaters of perennial streams. When occurring in association with Sedge Meadows, Northern White Cedar Swamps, Intermediate Fens, or other wetlands, Rich Fens generally occur on the upslope edge of the wetland complex where the influence of groundwater seepage is strongest. Rich Fens in Vermont are small—most documented examples are smaller than six acres.
Rich Fens may occur in isolation from other wetlands or as part of larger wetland complexes. Rich Fens are commonly found in small depressions, with very small surface watersheds, and typically form the headwaters of perennial streams. When occurring in association with Sedge Meadows, Northern White Cedar Swamps, Intermediate Fens, or other wetlands, Rich Fens generally occur on the upslope edge of the wetland complex where the influence of groundwater seepage is strongest. Rich Fens in Vermont are small—most documented examples are smaller than six acres.
Vegetation
Rich Fens are dominated by brown mosses and low sedges and grasses. Low shrub cover varies from sparse or absent in some fens to occasionally dense in others. Rich Fens may have scattered low hummocks with species characteristic of bogs.
The bryophyte component of Rich Fens is well developed, with moss cover generally close to 100 percent. Characteristic mosses are starry campylium, Scorpidium revolvens, Calliergonella cuspidata, Philonotis fontana, Ptychostomum pseudotriquetrum, and Tomenthypnum nitens.
The low, herbaceous cover is primarily sedges, with inland sedge, porcupine sedge, yellow sedge, and Hudson Bay bulrush present in most fens. Other characteristic herbs include bristle-stalked sedge, water avens, single-spike muhlenbergia, Kalm’s lobelia, golden ragwort, and blue flag. Many other herbaceous plants may be present. Red-osier dogwood is a shrub that occurs in most Rich Fens but is seldom very abundant. Shrubby cinquefoil and alder-leaved buckthorn are scattered across many fens, and they are locally abundant in others.
Wildlife Habitat
Breeding birds of Rich Fens include swamp sparrow, common yellowthroat, and Wilson’s snipe. Red-bellied snakes may be found on the margins of Rich Fens. Four-toed salamanders hide and lay their eggs in moist sphagnum and other mosses. The brilliantly-colored eastern red damsel is found in grassy openings with groundwater seepage. Two rare dragonflies of Rich Fens are ebony boghaunter and elfin skimmer.
Related Communities

- Poor Fens receive groundwater that is only slightly enriched with minerals. Poor fens are dominated by sphagnum mosses, sedges, and heath shrubs, and have well-developed hummocks and hollows. Peat depths are generally greater than those of Rich Fens.
- Intermediate Fens are enriched but slightly more acidic peatlands dominated by woolly-fruited sedge. Sweet gale is common and brown mosses are abundant. Sphagnum mosses and heath shrubs are uncommon, except on occasional hummocks. Peat depths are generally greater than those of Rich Fens.
Conservation Status and Management Considerations
Rich Fens are rare, both statewide and globally. Vermont has some of the highest quality examples of this community in the region, due in part to the extensive areas of calcareous bedrock in the state. Several Rich Fens are protected on conserved land. Vermont has a disproportionate number of examples of this rare community. All Rich Fens have global conservation significance and should be protected.
Many of Vermont’s Rich Fens have been altered in the past by grazing or hay-cropping, or are located adjacent to active agricultural fields where they may receive nutrient-rich runoff. Surface water runoff that is high in nitrogen or phosphorus can have a significant effect on the species composition of fens, leading to a decline in species richness and an increased abundance of generalist species like common cattail. As with other fen types and wetlands that receive mineral-enriched groundwater, Rich Fens are susceptible to changes in the quality or quantity of this groundwater input. Protection of fen communities requires protection of not just the small surface watershed, but also the area of groundwater recharge to the fen. The vegetation in fens is extremely susceptible to trampling. Visits should be limited to sites with boardwalks, or to the uplands adjacent to fens.
Although beavers are a form of natural disturbance in Rich Fens, their effects may be significantly increased by the presence of human infrastructure. Roads or raised trails that cross the outlet streams of fens are prime sites for beavers to construct dams. These roads or trails should be removed, if possible, or monitored closely for beaver activity. Given the rarity of this community and the abundance of rare species, managing beavers should be considered at all Rich Fens.
Distribution/Abundance 
Rich Fens in Vermont are restricted to areas with calcium-rich bedrock. Similar communities are found throughout northern New England, the Lake States, and north into Canada, but nowhere are they common—this is a globally rare community.
Characteristic Plants
Trees (Stunted)
Occasional Species
Tamarack – Larix laricina
Northern white cedar – Thuja occidentalis
Red maple – Acer rubrum
Shrubs
Occasional to Locally Abundant Species
Shrubby cinquefoil – Dasiphora fruticosa
Alder-leaved buckthorn – Rhamnus alnifolia
Red-osier dogwood – Cornus sericea
Hoary willow – Salix candida
Herbs
Abundant Species
Inland sedge – Carex interior
Porcupine sedge – Carex hystericina
Yellow sedge – Carex flava
Hudson Bay bulrush – Trichophorum alpinum
Occasional to Locally Abundant Species
Bristle-stalked sedge – Carex leptalea
Single-spike muhlenbergia – Muhlenbergia glomerata
Water avens – Geum rivale
Green-keeled cottongrass – Eriophorum viridicarinatum
Kalm’s lobelia – Lobelia kalmii
Golden ragwort – Packera aurea
Blue flag – Iris versicolor
Common horsetail – Equisetum arvense
Water horsetail – Equisetum fluviatile
Common cattail – Typha latifolia
Slender beakrush – Eleocharis tenuis
Wild strawberry – Fragaria virginiana
Starry false Solomon’s seal – Maianthemum stellatum
Bog goldenrod – Solidago uliginosa
Robbins’ ragwort – Packera schweinitziana
Tall meadow rue – Thalictrum pubescens
Beaked sedge – Carex utriculata
Grass of Parnassus – Parnassia glauca
Bog buckbean – Menyanthes trifoliata
Swamp thistle – Cirsium muticum
Bryophytes
Abundant Species
Starry campylium – Campylium stellatum
Occasional to Locally Abundant Species
Moss – Scorpidium revolvens
Moss – Calliergonella cuspidata
Moss – Philonotis fontana
Moss – Ptychostomum pseudotriquetrum
Moss – Tomenthypnum nitens
Moss – Sphagnum warnstorfii
Moss – Aulacomnium palustre
Moss – Hamatocaulis vernicosus
Moss – Calliergon giganteum
Rare and Uncommon Plants
Schweinitz’s sedge – Carex schweinitzii
Bog willow – Salix pedicellaris
Showy lady’s slipper – Cypripedium reginae
Few-flowered spikerush – Eleocharis quinqueflora
Slender cottongrass – Eriophorum gracile
Water sedge – Carex aquatilis var. substricta
Twig rush – Cladium mariscoides
Small yellow lady’s slipper – Cypripedium parviflorum var. makasin
Bog bedstraw – Galium labradoricum
Green adder’s mouth – Malaxis unifolia
Bog wintergreen – Pyrola asarifolia ssp. asarifolia
Hoary willow – Salix candida
Hooked scorpion moss – Scorpidium scorpioides
Moss – Elodium blandowii
Moss – Paludella squarrosa
Moss – Meesia triquetra
Moss – Cinclidium stygium
Moss – Pseudocalliergon trifarium
Moss – Tomenthypnum nitens
Moss – Tomenthypnum falcifoium
Associated Animals
Green frog – Lithobates clamitans
Red-bellied snake – Storeria occipitomaculata
Common yellowthroat – Geothlypis trichas
Swamp sparrow – Melospiza georgiana
Wilson’s snipe – Gallinago delicata
Eastern red damsel – Amphiagrion saucium
Rare and Uncommon Animals
Four-toed salamander – Hemidactylium scutatum
Spotted turtle – Clemmys guttata
Ebony boghaunter – Williamsonia fletcheri
Elfin skimmer – Nannothemis bella
Places to Visit
Eshqua Bog Natural Area, Hartland, Native Plant Trust, and The Nature Conservancy (TNC)
Chickering Bog Natural Area, Calais, TNC
