Fish
Fish Culture
State fish culture stations (hatcheries) stock close to 2 million fish annually in public waters for angling and fish restoration.

In addition to stocking fish for public waters, Vermont fish hatcheries:
Stop the Spread of AIS
When boating, fishing or recreating on Vermont waterways, you can help protect the health of aquatic ecosystems by taking these simple precautions.

Aquatic Invasive Species
 The introduction and spread of aquatic invasive species (AIS) impacts the health of Vermont's waterbodies and aquatic communities by changing the surrounding ecosystem, and out-competing native species for food and habitat.
The introduction and spread of aquatic invasive species (AIS) impacts the health of Vermont's waterbodies and aquatic communities by changing the surrounding ecosystem, and out-competing native species for food and habitat.
Fish Health Program
Vermont's Fish Health program helps protect wild fish populations and fish reared at fish culture stations by preventing and managing serious fish diseases.
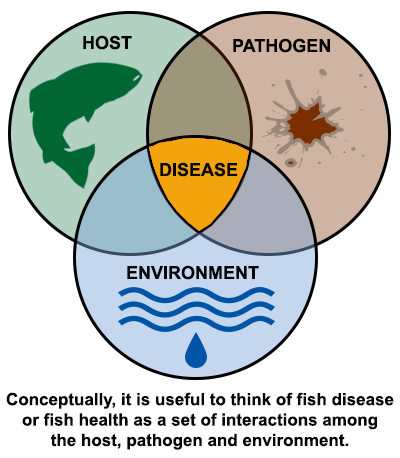
The program is responsible for:
USFWS Salmon Restoration Blogs
Learn about collaborative efforts to restore salmon to the Lake Champlain fisheries.
Fisheries Biologist Reports
Vermont's fisheries biologists are engaged in a variety of activities to ensure Vermont's valuable fisheries resources are sustained and enhanced through time.



